Form1099online.com is apporved by IRS as their certified efile service provider & tax partner for filing forms 1099-MISC, 1099-A, 1099-C, 1099-DIV, 1099-INT, 1099-K,1099-PATR and 1099-R
Welcome to form1099efile! E-File 1099 forms in 4 Minutes.
1.Register for Free 2.Select Form 3.Enter Info 4.Pay&Submit
GET STARTED FOR FREE
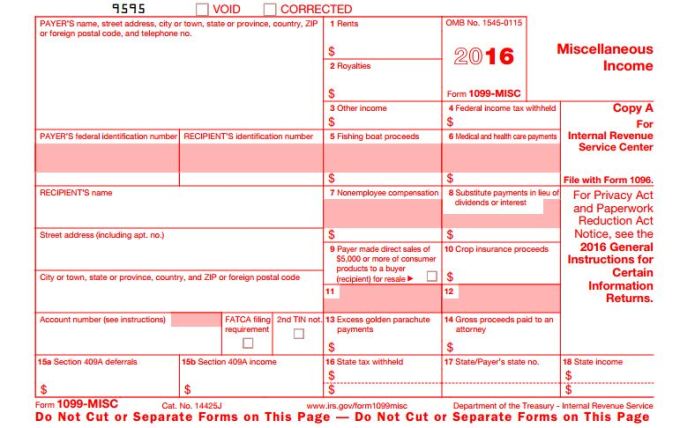
File Form 1099-MISC, Miscellaneous Income, for each person to whom you have paid during the year: At least $10 in royalties (see the instructions for box 2) or broker payments in lieu of dividends or tax-exempt interest (see the instructions for box 8); At least $600 in:
1. rents (box 1);
2. services performed by someone who is not your employee (including parts and materials), box 7;
3. prizes and awards (see instructions for boxes 3 and 7);
4. other income payments (box 3);
5. medical and health care payments (box 6);
6. crop insurance proceeds (box 10);
7. cash payments for fish (or other aquatic life) you purchase from anyone engaged in the trade or business of catching fish (box 7);
8. generally, the cash paid from a notional principal contract to an individual, partnership, or estate (box 3);
9. Payments to an attorney. See Payments to attorneys, later; or
10. Any fishing boat proceeds (box 5).
In addition, use Form 1099-MISC to report that you made direct sales of at least $5,000 of consumer products to a buyer for resale anywhere other than a permanent retail establishment (box 9). You must also file Form 1099-MISC for each person from whom you have withheld any federal income tax (report in box 4) under the backup withholding rules regardless of the amount of the payment.
Box 1. Rents
Enter amounts of $600 or more for all types of rents, such as any of the following.
Real estate rentals paid for office space. However, you do not have to report these payments on Form 1099-MISC if you paid them to a real estate agent. But the real estate agent must use Form 1099-MISC to report the rent paid over to the property owner. See Regulations section 1.6041-1(e)(5), Example 5.
Machine rentals (for example, renting a bulldozer to level your parking lot). If the machine rental is part of a contract that includes both the use of the machine and the operator, prorate the rental between the rent of the machine (report that in box 1) and the operator's charge (report that as nonemployee compensation in box 7).
Pasture rentals (for example, farmers paying for the use of grazing land).
Public housing agencies must report in box 1 rental assistance payments made to owners of housing projects. See Rev. Rul. 88-53, 1988-1 C.B. 384.
Coin-operated amusements. If an arrangement between an owner of coin-operated amusements and an owner of a business establishment where the amusements are placed is a lease of the amusements or the amusement space, the owner of the amusements or the owner of the space, whoever makes the payments, must report the lease payments in box 1 of Form 1099-MISC if the payments total at least $600. However, if the arrangement is a joint venture, the joint venture must file a Form 1065, U.S. Return of Partnership Income, and provide each partner with the information necessary to report the partner's share of the taxable income. Coin-operated amusements include video games, pinball machines, jukeboxes, pool tables, slot machines, and other machines and gaming devices operated by coins or tokens inserted into the machines by individual users. For more information, see Rev. Rul. 92-49, 1992-1 C.B. 433.
Box 2. Royalties
Enter gross royalty payments (or similar amounts) of $10 or more. Report royalties from oil, gas, or other mineral properties before reduction for severance and other taxes that may have been withheld and paid. Do not include surface royalties. They should be reported in box 1. Do not report oil or gas payments for a working interest in box 2; report payments for working interests in box 7. Do not report timber royalties made under a pay-as-cut contract; report these timber royalties on Form 1099-S, Proceeds From Real Estate Transactions. Use box 2 to report
Use box 2 to report royalty payments from intangible property such as patents, copyrights, trade names, and trademarks. Report the gross royalties (before reduction for fees, commissions, or expenses) paid by a publisher directly to an author or literary agent, unless the agent is a corporation. The literary agent (whether or not a corporation) that receives the royalty payment on behalf of the author must report the gross amount of royalty payments to the author on Form 1099-MISC whether or not the publisher reported the payment to the agent on its Form 1099-MISC.
Box 3. Other Income
Enter other income of $600 or more required to be reported on Form 1099-MISC that is not reportable in one of the other boxes on the form.
Also enter in box 3 prizes and awards that are not for services performed. Include the fair market value (FMV) of merchandise won on game shows. Also include amounts paid to a winner of a sweepstakes not involving a wager. If a wager is made, report the winnings on Form W-2G.
Do not include prizes and awards paid to your employees. Report these on Form W-2. Do not include in box 3 prizes and awards for services performed by nonemployees, such as an award for the top commission salesperson. Report them in box 7.
Do not include prizes and awards paid to your employees. Report these on Form W-2. Do not include in box 3 prizes and awards for services performed by nonemployees, such as an award for the top commission salesperson. Report them in box 7.
Prizes and awards received in recognition of past accomplishments in religious, charitable, scientific, artistic, educational, literary, or civic fields are not reportable if:
The winners are chosen without action on their part,
The winners are not expected to perform future services, and
The payer transfers the prize or award to a charitable organization or governmental unit under a designation made by the recipient. See Rev. Proc. 87-54, 1987-2 C.B. 669
. Other items required to be reported in box 3 include the following
1. Payments as explained earlier under Deceased employee's wages.
2. Payments as explained earlier under Indian gaming profits, payments to tribal members.
3. A payment or series of payments made to individuals for participating in a medical research study or
4. Termination payments to former self-employed insurance salespeople. These payments are not subject to self-employment tax and are reportable in box 3 (rather than box 7) if all the following apply.
a. The payments are received from an insurance company because of services performed as an insurance salesperson for the company.
b. The payments are received after termination of the salesperson's agreement to perform services for the company.
c. The salesperson did not perform any services for the company after termination and before the end of the year
. d. The salesperson enters into a covenant not to compete against the company for at least 1 year after the date of termination.
e. The amount of the payments depends primarily on policies sold by the salesperson or credited to the salesperson's account during the last year of the service agreement or to the extent those policies remain in force for some period after termination, or both.
f. The amount of the payments does not depend at all on length of service or overall earnings from the company (regardless of whether eligibility for payment depends on length of service).
If the termination payments do not meet all these requirements, report them in box 7.
5. Generally, all punitive damages, any damages for nonphysical injuries or sickness, and any other taxable damages. Report punitive damages even if they relate to physical injury or physical sickness. Generally, report all compensatory damages for nonphysical injuries or sickness, such as employment discrimination or defamation. However, do not report damages (other than punitive damages):
a. Received on account of personal physical injuries or physical sickness;
b. That do not exceed the amount paid for medical care for emotional distress;
c. Received on account of nonphysical injuries (for example, emotional distress) under a written binding agreement, court decree, or mediation award in effect on or issued by September 13, 1995; or
d. That are for a replacement of capital, such as damages paid to a buyer by a contractor who failed to complete construction of a building.
Damages received on account of emotional distress, including physical symptoms such as insomnia, headaches, and stomach disorders, are not considered received for a physical injury or physical sickness and are reportable unless described in (b) or (c) above. However, damages received on account of emotional distress due to physical injuries or physical sickness are not reportable.
Also report liquidated damages received under the Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967.
Foreign agricultural workers. Report in box 3 compensation of $600 or more paid in a calendar year to an H-2A visa agricultural worker who did not give you a valid taxpayer identification number. You must also withhold
federal income tax under the backup withholding rules. For more information, go to IRS.gov and enter “foreign agricultural workers” in the search box.
Account reported under FATCA. If you are an FFI reporting pursuant to an election described in Regulations section 1.1471-4(d)(5)(i)(A) a U.S. account required to be reported under chapter 4 to which during the year you made no payments reportable on an applicable Form 1099, enter zero in box 3. In addition, if you are an FFI described in the preceding sentence and, during the year, you made payments to the account required to be reported under chapter 4, but those payments are not reportable on an applicable Form 1099 (for example, because the payment is under the applicable reporting threshold), you must report the account on this Form 1099-MISC and enter zero in box 3
Box 4. Federal Income Tax Withheld
Enter backup withholding. For example, persons who have not furnished their TIN to you are subject to withholding on payments required to be reported in boxes 1, 2 (net of severance taxes), 3, 5 (to the extent paid in cash), 6, 7 (except fish purchases for cash), 8, 10, and 14. For more information on backup withholding, including the rate, see part N in the 2016 General Instructions for Certain Information Returns.
Also enter any income tax withheld from payments to members of Indian tribes from the net revenues of class II or class III gaming activities conducted or licensed by the tribes.
Box 5. Fishing Boat Proceeds
Enter the individual's share of all proceeds from the sale of a catch or the FMV of a distribution in kind to each crew member of fishing boats with normally fewer than 10 crew members. A fishing boat has normally fewer than 10 crew members if the average size of the operating crew was fewer than 10 on trips during the preceding 4 calendar quarters.
In addition, report cash payments of up to $100 per trip that are contingent on a minimum catch and are paid solely for additional duties (such as mate, engineer, or cook) for which additional cash payments are traditional in the industry. However, do not report on Form 1099-MISC any wages reportable on Form W-2.
Box 6. Medical and Health Care Payments
Enter payments of $600 or more made in the course of your trade or business to each physician or other supplier or provider of medical or health care services. Include payments made by medical and health care insurers under health, accident, and sickness insurance programs. If payment is made to a corporation, list the corporation as the recipient rather than the individual providing the services. Payments to persons providing health care services often include charges for injections, drugs, dentures, and similar items. In these cases the entire payment is subject to information reporting. You are not required to report payments to pharmacies for prescription drugs.
The exemption from issuing Form 1099-MISC to a corporation does not apply to payments for medical or health care services provided by corporations, including professional corporations. However, you are not required to report payments made to a tax-exempt hospital or extended care facility or to a hospital or extended care facility owned and operated by the United States (or its possessions), a state, the District of Columbia, or any of their political subdivisions, agencies, or instrumentalities.
Box 7. Nonemployee Compensation
Enter nonemployee compensation of $600 or more. Include fees, commissions, prizes and awards for services performed as a nonemployee, other forms of compensation for services performed for your trade or business by an individual who is not your employee, and fish purchases for cash. Include oil and gas payments for a working interest, whether or not services are performed. Also include expenses incurred for the use of an entertainment facility that you treat as compensation to a nonemployee. Federal CAUTION ! executive agencies that make payments to vendors for services, including payments to corporations, must report the payments in this box. See Rev. Rul. 2003-66, which is on page 1115 of Internal Revenue Bulletin 2003-26 at www.irs.gov/pub/irs-irbs/irb03-26.pdf.
What is nonemployee compensation? If the following four conditions are met, you must generally report a payment as nonemployee compensation.
You made the payment to someone who is not your employee.
You made the payment for services in the course of your trade or business (including government agencies and nonprofit organizations).
You made the payment to an individual, partnership, estate, or, in some cases, a corporation.
You made payments to the payee of at least $600 during the year.

Self-employment tax. Generally, amounts reportable in box 7 are subject to self-employment tax. If payments to individuals are not subject to this tax and are not reportable elsewhere on Form 1099-MISC, report the payments in box 3. However, report section 530 (of the Revenue Act of 1978) worker payments in box 7.
Examples. The following are some examples of payments to be reported in box 7. Professional service fees, such as fees to attorneys (including corporations), accountants, architects, contractors, engineers, etc.
Fees paid by one professional to another, such as fee-splitting or referral fees.
Payments by attorneys to witnesses or experts in legal adjudication.
Payment for services, including payment for parts or materials used to perform the services if supplying the parts or materials was incidental to providing the service. For example, report the total insurance company payments to an auto repair shop under a repair contract showing an amount for labor and another amount for parts, if furnishing parts was incidental to repairing the auto.
Commissions paid to nonemployee salespersons that are subject to repayment but not repaid during.
A fee paid to a nonemployee, including an independent contractor, or travel reimbursement for which the nonemployee did not account to the payer, if the fee and reimbursement total at least $600. To help you determine whether someone is an independent contractor or an employee, see Pub. 15-A.
Payments to nonemployee entertainers for services. Use Form 1042-S, Foreign Person's U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding, for payments to nonresident aliens.
Exchanges of services between individuals in the course of their trades or businesses. For example, an attorney represents a painter for nonpayment of business debts in exchange for the painting of the attorney's law offices. The amount reportable by each on Form 1099-MISC is the FMV of his or her own services performed. However, if the attorney represents the painter in a divorce proceeding, this is an activity that is unrelated to the painter's trade or business.
The attorney must report on Form 1099-MISC the value of his or her services. But the painter need not report on Form 1099-MISC the value of painting the law offices because the work is in exchange for legal services that are separate from the painter's business.
Taxable fringe benefits for nonemployees. For information on the valuation of fringe benefits, see Pub. 15-B, Employer's Tax Guide to Fringe Benefits.
Gross oil and gas payments for a working interest.
Payments to an insurance salesperson who is not your common law or statutory employee. See Pub. 15-A for the definition of employee. However, for termination payments to former insurance salespeople, see the instructions for box 3.
Directors' fees as explained under Directors' fees, earlier.
Commissions paid to licensed lottery ticket sales agents as explained under Commissions paid to lottery ticket sales agents, earlier.
Payments to section 530 (of the Revenue Act of 1978) workers. See the TIP under Independent contractor or employee, earlier.
Fish purchases for cash. See Fish purchases, earlier.
Nonqualified deferred compensation (section 409A) income. Include in box 7 the amount of all deferrals (plus earnings) reported in box 15b that are includible in gross income because the nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plan fails to satisfy the requirements of section 409A. See Regulations sections 1.409A-1 through 1.409A-6.
Golden parachute payments. A parachute payment is any payment that meets all of the following conditions.
1. The payment is in the nature of compensation.
2. The payment is to, or for the benefit of, a disqualified individual.
3. The payment is contingent on a change in the ownership of a corporation, the effective control of a corporation, or the ownership of a substantial portion of the assets of a corporation (a change in ownership or control).
4. The payment has (together with other payments described in (1), (2), and (3), above, made to the same individual) an aggregate present value of at least three times the individual's base amount.
A disqualified individual is one who at any time during the 12-month period prior to and ending on the date of the change in ownership or control of the corporation (the disqualified individual determination period) was an employee or independent contractor and was, in regard to that corporation, a shareholder, an officer, or a highly compensated individual.
For more details, see Regulations section 1.280G-1. Also, see Rev. Proc. 2003-68, which is on page 398 of Internal Revenue Bulletin 2003-34 at www.irs.gov/pub/irs-irbs/ irb03-34.pdf, concerning the valuation of stock options for purposes of golden parachute payment rules. For the treatment of unvested shares of restricted stock, see Rev. Rul. 2005-39, available at www.irs.gov/irb/2005-27_IRB/ ar08.html.
Independent contractor. Enter in box 7 the total compensation, including any golden parachute payment. For excess golden parachute payments, see the box 13 reporting instructions.
For employee reporting of these payments, see Pub. 15-A.
Payments not reported in box 7. Do not report in box 7:
expense reimbursements paid to volunteers of non-profit organizations;
deceased employee wages paid in the year after death (report in box 3)(See Deceased employee's wages, earlier);
payments more appropriately described as rent (report in box 1), royalties (report in box 2), other income not subject to self-employment tax (report in box 3), interest (use Form 1099-INT);
the cost of current life insurance protection (report on Form W-2 or Form 1099-R);
an employee's wages, travel or auto allowance, or bonuses and prizes (report on Form W-2); and
the cost of group-term life insurance paid on behalf of a former employee (report on Form W-2).
Box 8. Substitute Payments in Lieu of Dividends or Interest
Enter aggregate payments of at least $10 received by a broker for a customer in lieu of dividends or tax-exempt interest as a result of a loan of a customer's securities. For this purpose, a customer includes an individual, trust, estate, partnership, association, company, or corporation. See Notice 2003-67, which is on page 752 of Internal Revenue Bulletin 2003-40 at www.irs.gov/pub/irs-irbs/irb03-40.pdf. It does not include a tax-exempt organization, the United States, any state, the District of Columbia, a U.S. possession, or a foreign government. File Form 1099-MISC with the IRS and furnish a copy to the customer for whom you received the payment. Also, file Form 1099-MISC for and furnish a copy to an individual for whom you received a payment in lieu of tax-exempt interest.
Substitute payment means a payment in lieu of (a) a dividend, or (b) tax-exempt interest to the extent that interest (including OID) has accrued while the securities were on loan.
Box 9. Payer Made Direct Sales of $5,000 or More
Enter an “X” in the checkbox for sales by you of $5,000 or more of consumer products to a person on a buy-sell, deposit-commission, or other commission basis for resale (by the buyer or any other person) anywhere other than in a permanent retail establishment. Do not enter a dollar amount in this box.
If you are reporting an amount in box 7, you may also check box 9 on the same Form 1099-MISC. -8- Instructions for Form 1099-MISC.
The report you must give to the recipient for these direct sales need not be made on the official form. It may be in the form of a letter showing this information along with commissions, prizes, awards, etc.
Box 10. Crop Insurance Proceeds
Enter crop insurance proceeds of $600 or more paid to farmers by insurance companies unless the farmer has informed the insurance company that expenses have been capitalized under section 278, 263A, or 447.
Box 13. Excess Golden Parachute Payments
Enter any excess golden parachute payments. An excess parachute payment is the amount of the excess of any parachute payment over the base amount (the average annual compensation for services includible in the individual's gross income over the most recent 5 tax years). See Q/A-38 through Q/A-44 of Regulations section 1.280G-1 for how to compute the excess amount.
See Golden parachute payments, earlier, for more information.
Box 14. Gross Proceeds Paid to an Attorney
Enter gross proceeds of $600 or more paid to an attorney in connection with legal services (regardless of whether the services are performed for the payer). See Payments to attorneys, earlier.
Box 15a. Section 409A Deferrals
You do not have to complete this box. For details, see Notice 2008-115, available at www.irs.gov/irb/2008-52_IRB/ ar10.html.
If you complete this box, enter the total amount deferred during the year of at least $600 for the nonemployee under all nonqualified plans. The deferrals during the year include earnings on the current year and prior year deferrals. For additional information, see Regulations sections 1.409A-1 through 1.409A-6.
For deferrals and earnings under NQDC plans for employees, see the Instructions for Forms W-2 and W-3.
Box 15b. Section 409A
Income Enter all amounts deferred (including earnings on amounts deferred) that are includible in income under section 409A because the NQDC plan fails to satisfy the requirements of section 409A. Do not include amounts properly reported on a Form 1099-MISC, corrected Form 1099-MISC, Form W-2, or Form W-2c for a prior year. Also, do not include amounts that are considered to be subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture for purposes of section 409A. For additional information, see Regulations sections 1.409A-1 through 1.409A-6; Notice 2008-113, available at www.irs.gov/irb/2008-51_IRB/ ar12.html; Notice 2008-115; Notice 2010-6, which is available at www.irs.gov/irb/2010-03_IRB/ar08.html; and Notice 2010-80, available at www.irs.gov/irb/2010-51_IRB/ ar08.html.
The amount included in box 15b is also includible in box 7
Boxes 16–18. State Information
These boxes may be used by payers who participate in the Combined Federal/State Filing Program and/or who are required to file paper copies of this form with a state tax department. See Pub. 1220 for more information regarding the Combined Federal/State Filing Program. They are provided for your convenience only and need not be completed for the IRS. Use the state information boxes to report payments for up to two states. Keep the information for each state separated by the dash line. If you withheld state income tax on this payment, you may enter it in box 16. In box 17, enter the abbreviated name of the state and the payer's state identification number. The state number is the payer's identification number assigned by the individual state. In box 18, you may enter the amount of the state payment.
If a state tax department requires that you send them a paper copy of this form, use Copy 1 to provide information to the state tax department. Give Copy 2 to the recipient for use in filing the recipient's state income tax return

Thanks for sharing your experience. Such very useful blog. If you want more info 1099 MISC Form Online
ReplyDelete